Ace Fortinet FCP - Azure Cloud Security 7.4 Administrator: Your FCP_ZCS_AD-7.4 Success Blueprint
Refer to the exhibit.
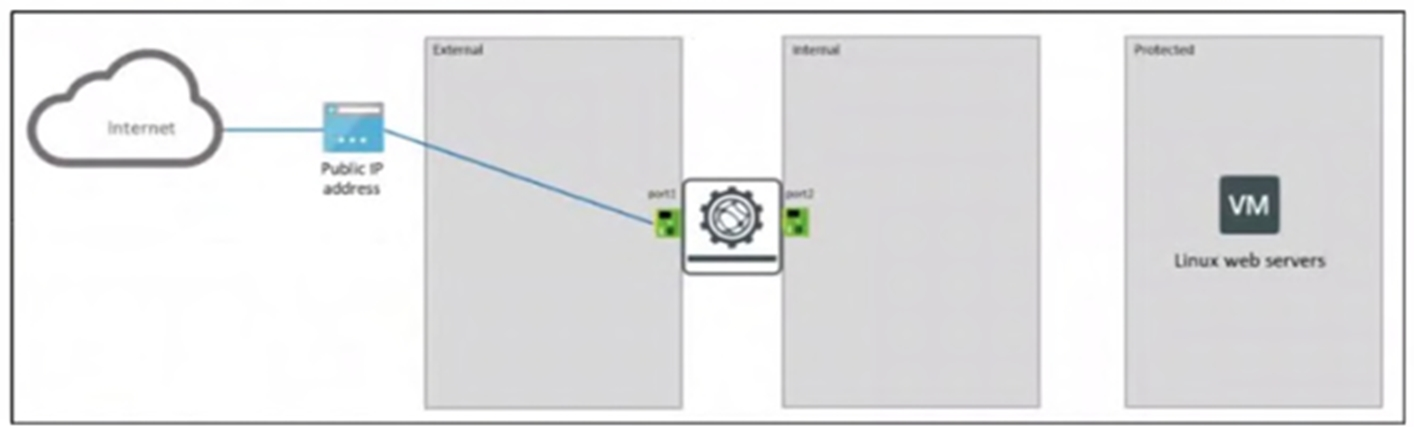
Your company runs front-end web servers in Azure. You need to deploy a Linux VM to be used as a web server.
To protect your web servers with a web application firewall (WAF), you deploy FortiWeb to secure applications from web-based attacks.
Which FortiWeb operation mode can you implement for this scenario?
Correct : A
The Reverse Proxy mode is the most appropriate FortiWeb operation mode for this scenario. In this mode, FortiWeb sits between internet users and the Linux web servers, terminating client connections and then forwarding requests to the backend servers. This enables deep inspection, protection from web attacks (like SQL injection and XSS), and full WAF functionality, making it ideal for securing front-end web servers exposed to the internet.
Start a Discussions
Which statement about deploying VMs in a gateway subnet is true?
Correct : A
Azure does not allow the deployment of virtual machines (VMs) in a gateway subnet. The gateway subnet is specifically reserved for Azure VPN Gateway or ExpressRoute Gateway instances, and deploying other resources in it can cause gateway deployment or operation failures.
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibit.
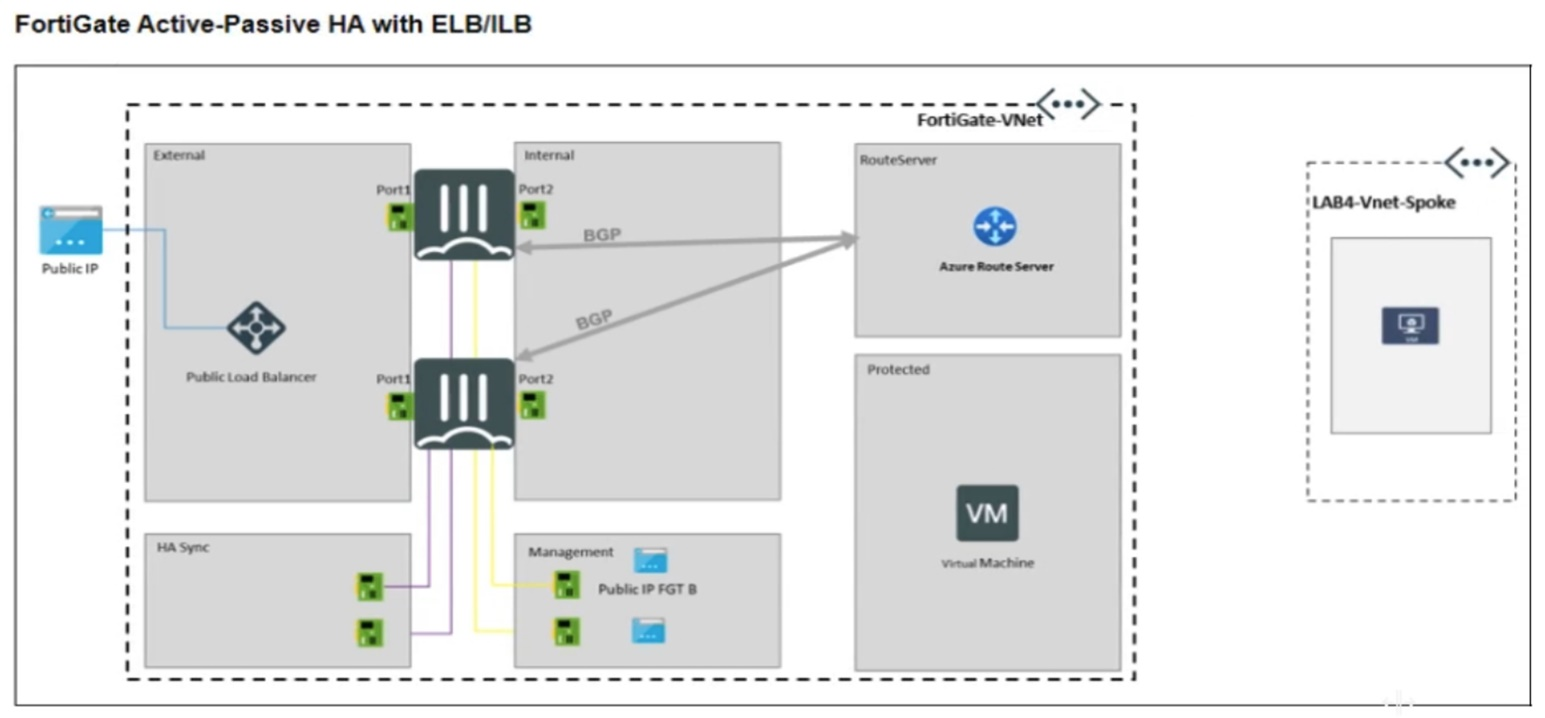
An Azure Route Server and an active-passive FortiGate with Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) and Internal Load Balancing (ILB) have been deployed successfully and they are sharing and populating BGP routes in the Protected VNet.
A Linux server has been deployed in a new VNet spoke. It is expected that Azure Route Server
should inject the FortiGate BGP routes into the Linux server but that failed.
How can you diagnose the problem?
Correct : A
The Linux server in the spoke VNet cannot directly peer BGP with the Azure Route Server, as it is not a BGP-enabled device. Instead, Azure propagates routes to VMs through the effective route tables associated with their network interfaces (NICs). Therefore, to diagnose why BGP routes are not reaching the Linux VM, you should monitor the effective routes on the NIC to verify if the routes from the FortiGate (via the Route Server) are being injected properly.
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibits.

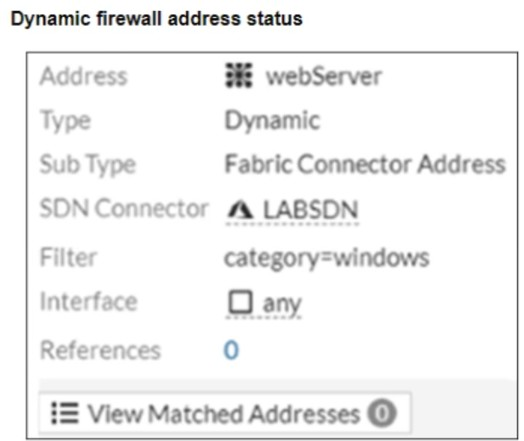
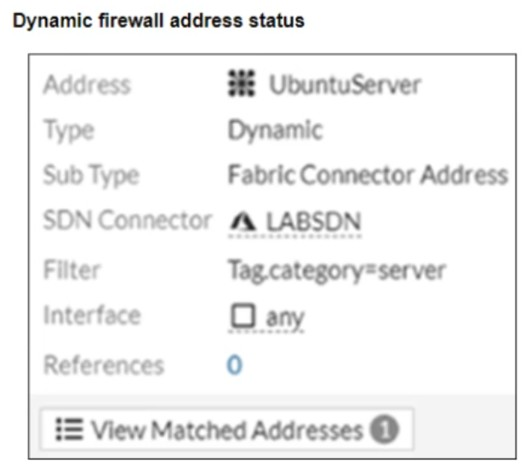
Two new dynamic firewall addresses have been configured on the FortiGate VM using the external connector to Integrate within the same Azure environment.
The debug output shows that one IP address can be resolved successfully, but the second is empty.
Which steps could you perform to correct the misconfiguration? (Choose all that apply.)
Correct : A, B
The debug output shows that the UbuntuServer address object successfully resolved an IP, while the webServer did not. The most likely cause is a mismatch in the dynamic address filter or missing tags on the target VM.
Verify the filter used for the dynamic firewall address -- The filter category=windows may not match any VM metadata, resulting in no matched addresses.
Verify the tags on the target VM -- Ensure that the VM has the correct tags (e.g., category=windows) that match the dynamic address filter to enable resolution.
Start a Discussions
When you deploy a single FortiGate VM using the available template from the Azure Marketplace, several other resources are also created.
Which two resources, among others, are created during the process? (Choose two.)
Correct : A, B
Two virtual NICs -- The FortiGate Azure Marketplace template deploys the VM with at least two network interfaces: one for the external/public interface and one for the internal/private interface.
One NSG for each interface -- The deployment creates separate Network Security Groups (NSGs) attached to each NIC to control inbound and outbound traffic as per Fortinet's best practices.
Start a Discussions
Total 35 questions