Unlock Fortinet Mastery: FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator Prep That Ignites Success
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a network diagram showing the addition of site 2 with an overlapping network segment to the existing VPN IPsec connection between the hub and site 1.
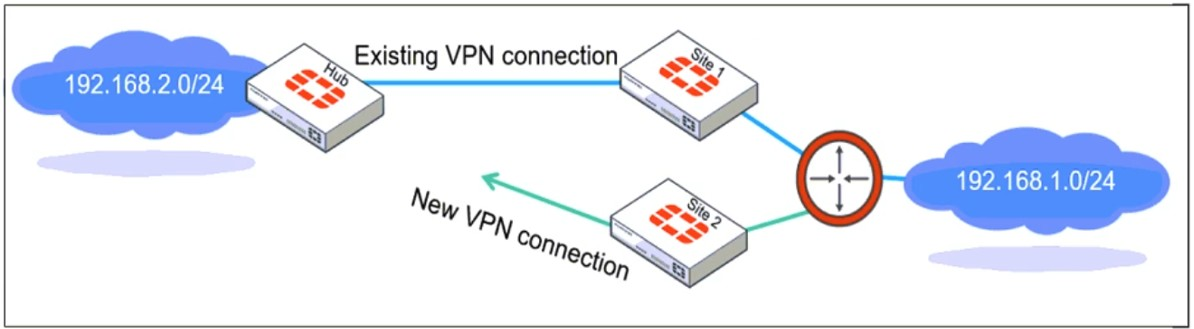
Which IPsec phase 2 configuration must an administrator make on the FortiGate hub to enable equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) routing when multiple remote sites connect with overlapping subnets?
Correct : A
When multiple remote sites connect to the same hub using overlapping subnets, FortiGate needs to determine which route should be used for traffic forwarding. The route-overlap setting in IPsec Phase 2 allows FortiGate to handle this scenario by deciding whether to keep the existing route (use-old) or replace it with a new route (use-new).
In an ECMP (Equal-Cost Multi-Path) routing setup, both routes should be retained and balanced, but FortiGate does not support ECMP directly over overlapping routes in IPsec Phase 2. Instead, an administrator must decide which connection takes precedence using route-overlap settings.
Start a Discussions
An administrator wants to scale the IBGP sessions and optimize the routing table in an IBGP network.
Which parameter should the administrator configure?
Correct : D
In an IBGP (Internal BGP) network, all routers must be fully meshed, meaning every router must establish a BGP session with every other router in the same autonomous system (AS). This does not scale well in large networks due to the exponential increase in BGP sessions.
To optimize and scale IBGP, Route Reflectors (RRs) are used. A Route Reflector (RR) reduces the number of IBGP peer connections by allowing a centralized router (RR) to redistribute IBGP routes to other IBGP peers (called clients). This eliminates the need for a full mesh, significantly reducing BGP session overhead.
By configuring the route-reflector-client setting on IBGP peers, an administrator can:
Scale IBGP sessions by reducing the number of direct BGP peer connections.
Optimize the routing table by ensuring routes are efficiently propagated within the IBGP network.
Eliminate the need for full mesh topology, making IBGP more manageable.
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibits.
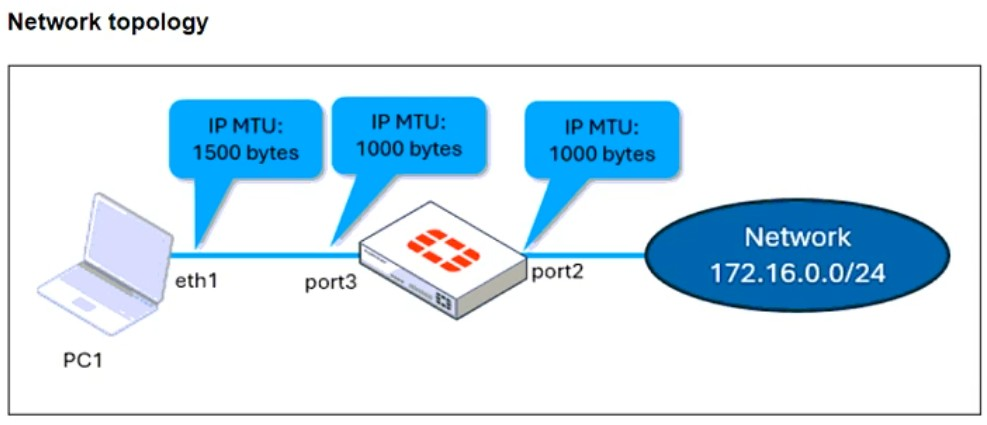
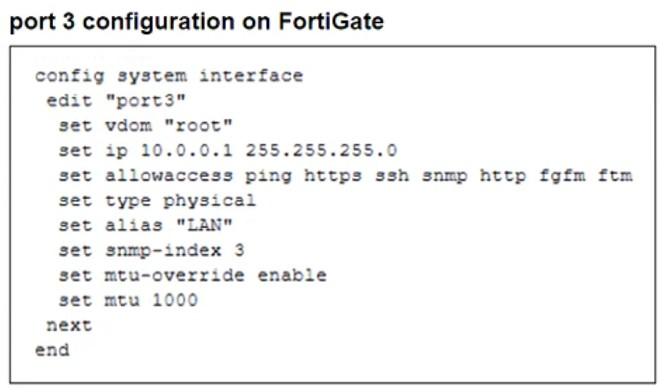
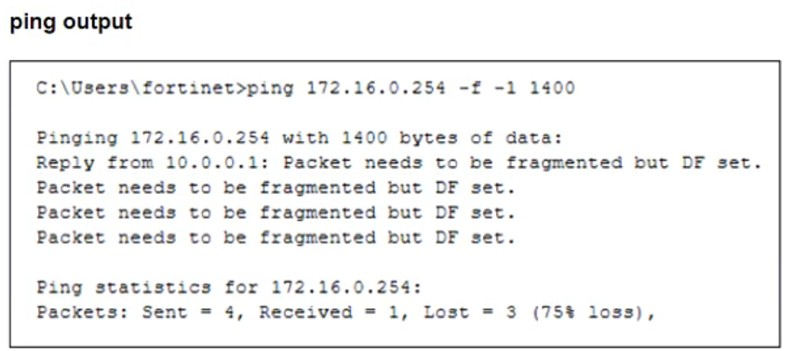
The configuration of a user's Windows PC, which has a default MTU of 1500 bytes, along with FortiGate interfaces set to an MTU of 1000 bytes, and the results of PC1 pinging server 172.16.0.254 are shown.
Why is the user in Windows PC1 unable to ping server 172.16.0.254 and is seeing the message: Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set?
Correct : C
The issue occurs because FortiGate enforces the 'do not fragment' (DF) bit in the packet, and the packet size exceeds the MTU of the network path. When the Windows PC1 (with an MTU of 1500 bytes) attempts to send a 1400-byte packet, the FortiGate interface (with an MTU of 1000 bytes) needs to fragment it. However, since the DF bit is set, FortiGate drops the packet instead of fragmenting it.
To resolve this, the user should adjust the ping packet size to fit within the path MTU. In this case, reducing the packet size to 972 bytes (1000 bytes MTU minus 28 bytes for the IP and ICMP headers) should allow successful transmission.
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the VDOM section of a FortiGate device.
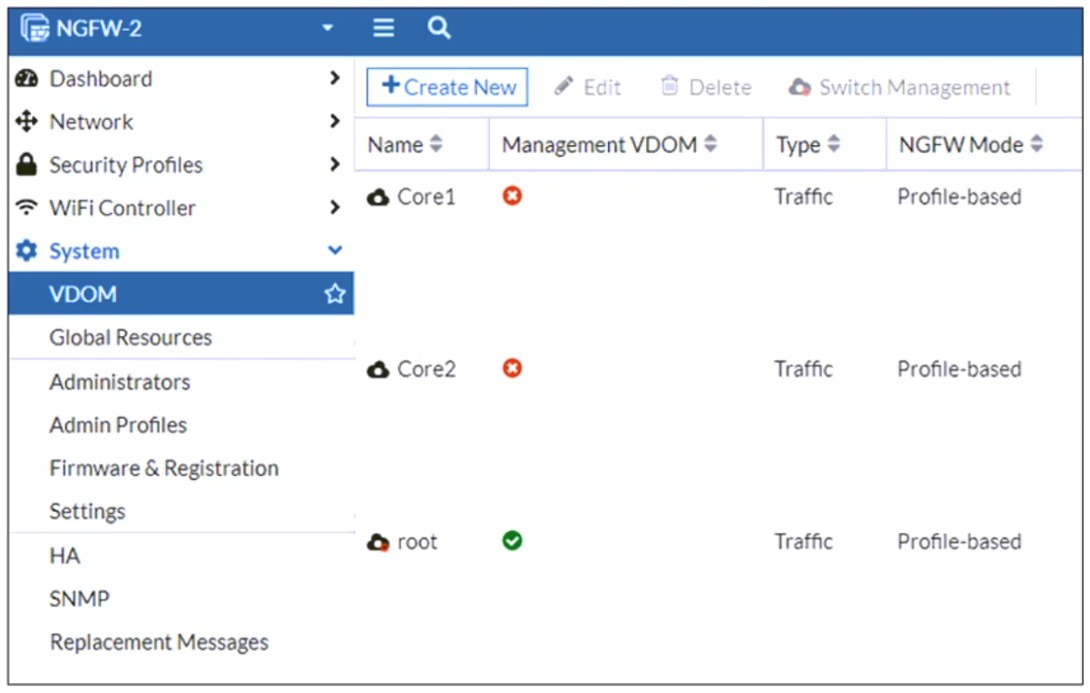
An administrator discovers that webfilter stopped working in Core1 and Core2 after a maintenance window.
Which two reasons could explain why webfilter stopped working? (Choose two.)
Correct : B, D
Since Core1 and Core2 are not designated as management VDOMs, they rely on the root VDOM for connectivity to external resources such as FortiGuard updates. If the root VDOM lacks a VDOM link to these VDOMs or cannot reach FortiGuard services, security features like web filtering will stop working.
Start a Discussions
Refer to the exhibit.
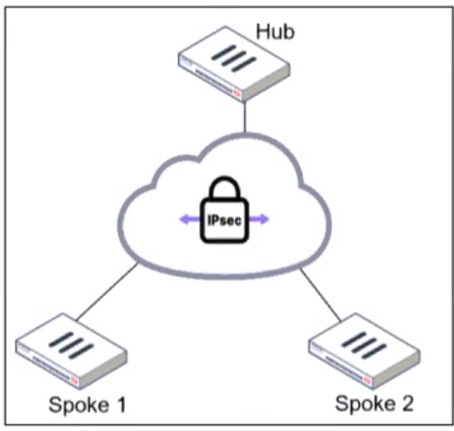
An administrator is deploying a hub and spokes network and using OSPF as dynamic protocol.
Which configuration is mandatory for neighbor adjacency?
Correct : B
In a hub-and-spoke topology using OSPF over IPsec VPNs, the point-to-multipoint network type is necessary to establish neighbor adjacencies between the hub and spokes. This network type ensures that OSPF operates correctly without requiring a designated router (DR) and allows dynamic routing updates across the IPsec tunnels.
Start a Discussions
Total 57 questions