Master Juniper Enterprise Routing and Switching with JN0-351 Specialist Prep
You are troubleshooting a BGP routing issue between your network and a customer router and are reviewing the BGP routing policies. Which two statements are correct in this scenario? (Choose two.)
Correct : C, D
In BGP, routing policies are used to control the flow of routing information between BGP peers1.
Therefore, options C and D are correct.
Start a Discussions
You are asked to connect an IP phone and a user computer using the same interface on an EX Series switch. The traffic from the computer does not use a VLAN tag, whereas the traffic from the IP phone uses a VLAN tag.
Which feature enables the interface to receive both types of traffic?
Correct : D
Start a Discussions
Exhibit
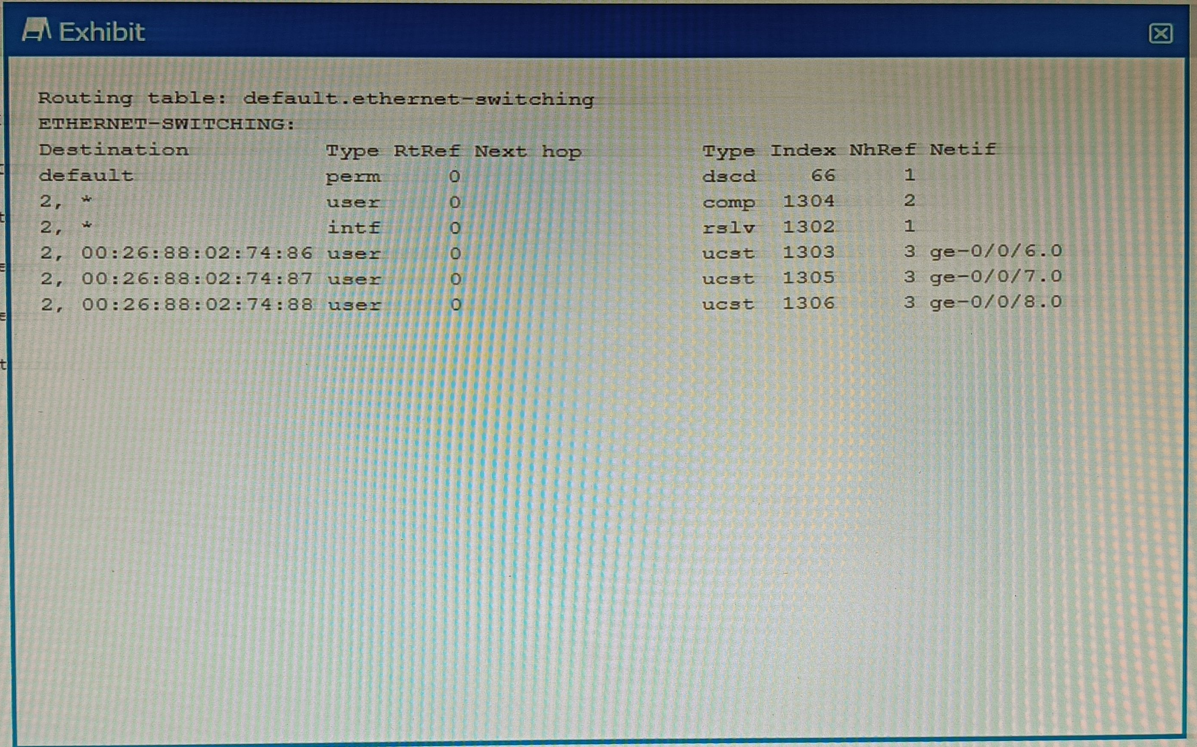
Which command displays the output shown in the exhibit?
Correct : B
Start a Discussions
You deployed a new EX Series switch with DHCP snooping enabled and you do not see any entries in the snooping databases for an interface. Which two Juniper configurations for that interface caused this issue? (Choose two.)
Correct : A, C
Start a Discussions
You have DHCP snooping enabled but no entries are automatically created in the snooping database for an interface on your EX Series switch. What are two reasons for the problem? (Choose two.)
Correct : B, C
However, there are certain conditions that could prevent entries from being automatically created in the snooping database for an interface:
Start a Discussions
Total 65 questions