Master Juniper Data Center Professional JN0-683: Your Gateway to Network Mastery
You are asked to automatically provision new Juniper Networks devices in your network with minimal manual intervention Before you begin, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Correct : A, D
Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP):
ZTP is a feature that allows for the automatic provisioning of devices with minimal manual intervention. It is widely used in large-scale deployments to quickly bring new devices online.
Key Requirements for ZTP:
A . DHCP Server: A DHCP server is crucial for ZTP as it provides the necessary information to new devices, such as the IP address, the location of the software image, and configuration files.
D . File Server: The file server is where the software image and configuration files are stored. The device downloads these files during the provisioning process.
Incorrect Options:
B . Syslog Server: While a syslog server is important for logging and monitoring, it is not a requirement for the initial provisioning process.
C . NTP Server: An NTP server is used for time synchronization, which is essential for accurate logging and operation but not specifically required for ZTP.
Data Center Reference:
ZTP simplifies the deployment process by automating the initial configuration steps, relying heavily on DHCP for communication and a file server for delivering the necessary configuration and software.
Start a Discussions
You are selling up an EVPN-VXLAN architecture (or your new data center. this initial deployment will be less than 50 switches: however, it could scale up to 250 switches over time supporting 1024 VLANs. You are still deciding whether to use symmetric or asymmetric routing.
In this scenario, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Correct : C, D
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Routing in EVPN-VXLAN:
Symmetric Routing: Traffic enters and exits the VXLAN network through the same VTEP, regardless of the source or destination. This approach simplifies routing decisions, especially in large networks, and is generally more scalable.
Asymmetric Routing: The routing occurs on the egress VTEP. This method can be simpler to deploy in smaller environments but becomes complex as the network scales, particularly with larger numbers of VNIs and VLANs.
Correct Statements:
C . Symmetric routing supports higher scaling numbers: Symmetric routing is preferred in larger EVPN-VXLAN deployments because it centralizes routing decisions, which can be more easily managed and scaled.
D . Asymmetric routing routes traffic on the egress switch: This is accurate, as asymmetric routing means the routing decision is made at the final hop, i.e., the egress VTEP before the traffic reaches its destination.
Incorrect Statements:
A . Symmetric routing needs an extra VLAN with an IRB interface for each L3 VRF instance: This is not accurate. Symmetric routing does not require an extra VLAN per VRF; rather, it uses the same VLAN/VNI across the network, simplifying routing and VLAN management.
B . Asymmetric routing is easier to monitor because of the transit VNI: Asymmetric routing is not necessarily easier to monitor; in fact, it can add complexity due to the split routing logic between ingress and egress points.
Data Center Reference:
The choice between symmetric and asymmetric routing in an EVPN-VXLAN environment depends on network size, complexity, and specific operational requirements. Symmetric routing is generally more scalable and easier to manage in large-scale deployments.
Start a Discussions
Your organization is implementing EVPN-VXLAN and requires multiple overlapping VLAN-IDs. You decide to use a routing-instance type mac-vrf to satisfy this request.
Which two statements are correct in this scenario? (Choose two.)
Correct : A, D
Understanding the Scenario:
EVPN-VXLAN deployments often involve scenarios where multiple tenants or applications require overlapping VLAN IDs, which can be managed using the mac-vrf routing instance type. This allows you to segregate traffic within the same VLAN ID across different tenants.
Host-facing Interface Configuration:
A . Host-facing interfaces must be configured using a service-provider style configuration: This is correct. In mac-vrf configurations, host-facing interfaces (those connecting end devices) typically follow a service-provider style configuration, where each customer or tenant's traffic is isolated even if overlapping VLAN IDs are used.
B . Host-facing interfaces must be configured using enterprise-style configuration: This is incorrect for mac-vrf instances because enterprise-style configurations are more common in simpler, less segmented networks.
Routing Instance Service Type:
D . The routing-instance service type can be VLAN-based: This is correct. The service type in mac-vrf can indeed be VLAN-based, which is particularly useful in scenarios where VLAN ID overlap is needed between different tenants or services.
Data Center Reference:
The mac-vrf instance type is powerful for handling complex multi-tenant environments in EVPN-VXLAN, especially when dealing with overlapping VLAN IDs across different segments of the network.
Start a Discussions
You are using a single tenant data center with a bridged overlay architecture. In this scenario, how do hosts of the different virtual networks communicate with each other?
Correct : A
Understanding Bridged Overlay Architecture:
In a single-tenant data center using a bridged overlay architecture, virtual networks (VLANs) are typically isolated within the fabric, with traffic between these VLANs handled outside the fabric.
Communication Between Different Virtual Networks:
A . off-fabric using an external device: This is correct. In many bridged overlay architectures, communication between different virtual networks is handled off-fabric, often using an external router or firewall that connects the different VLANs. The fabric itself primarily provides Layer 2 connectivity within each VLAN, leaving inter-VLAN routing to be handled externally.
Data Center Reference:
This design is common in smaller or simpler data center environments where a single tenant does not require complex on-fabric routing and prefers to handle inter-VLAN routing through dedicated devices.
Start a Discussions
Exhibit.
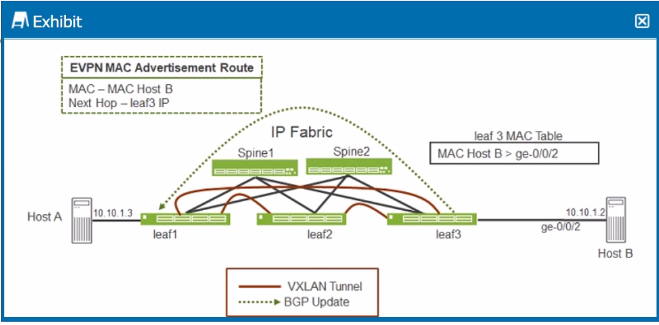
Referring to the exhibit, when Host A sends an ARP request for Host B's IP address, which Junos feature does leaf1 require to send an ARP response back to Host A without having to send a broadcast frame over the fabric?
Correct : A
Scenario Overview:
In the exhibit, Host A is trying to resolve Host B's IP address (10.10.1.2) through ARP (Address Resolution Protocol). Normally, an ARP request would be broadcasted over the network, and the host owning the IP address (Host B) would respond.
Role of Proxy ARP:
Option A: Proxy ARP allows a router or switch (in this case, leaf1) to respond to ARP requests on behalf of another host. Leaf1, knowing the MAC address of Host B through the EVPN MAC advertisement, can reply to Host A's ARP request directly without broadcasting the request across the entire network fabric. This feature reduces unnecessary traffic and increases network efficiency.
Conclusion:
Option A: Correct---Proxy ARP enables leaf1 to respond to Host A's ARP request for Host B's IP without broadcasting over the IP fabric, thus providing the ARP response locally.
Start a Discussions
Total 65 questions