Unlock Juniper SP Routing & Switching Mastery: Ace JN0-664 Pro Exam
Exhibit
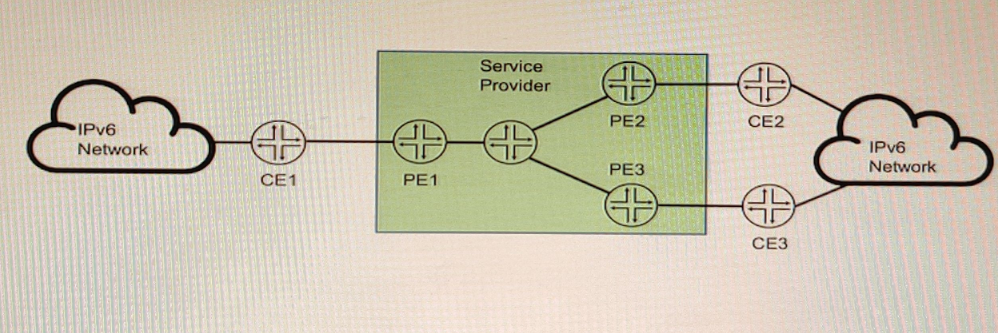
You are running a service provider network and must transport a customer's IPv6 traffic across your IPv4-based MPLS network using BGP You have already configured mpis ipv6-tunneling on your PE routers.
Which two statements are correct about the BGP configuration in this scenario? (Choose two.)
Correct : A, B
To transport IPv6 traffic over an IPv4-based MPLS network using BGP, you need to configure two address families: family inet6 labeled-unicast and family inet6 unicast. The former is used to exchange IPv6 routes with MPLS labels between PE routers, and the latter is used to exchange IPv6 routes without labels between PE and CE routers. The mpis ipv6-tunneling command enables the PE routers to encapsulate the IPv6 packets with an MPLS label stack and an IPv4 header before sending them over the MPLS network.
Start a Discussions
You are a network architect for a service provider and want to offer Layer 2 services to your customers You want to use EVPN for Layer 2 services in your existing MPLS network.
Which two statements are correct in this scenario? (Choose two.)
Correct : C, D
EVPN is a technology that connects L2 network segments separated by an L3 network using a virtual Layer 2 network overlay over the Layer 3 network. EVPN uses BGP as its control protocol to exchange different types of routes for different purposes. Type 2 routes are used to advertise MAC address and IP address pairs learned using ARP snooping from the local CE devices. Type 3 routes are used to join a multicast tree to flood traffic such as broadcast, unknown unicast, and multicast (BUM) traffic.
Start a Discussions
Exhibit

CE-1 and CE-2 are part of a VPLS called Customer1 No connectivity exists between CE-1 and CE-2. In the process of troubleshooting, you notice PE-1 is not learning any routes for this VPLS from PE-2, and PE-2 is not learning any routes for this VPLS from PE-1.
Correct : A
VPLS is a technology that provides Layer 2 VPN services over an MPLS network. VPLS uses BGP as its control protocol to exchange VPN membership information between PE routers. The route target is a BGP extended community attribute that identifies which VPN a route belongs to. The route target must match on PE routers that participate in the same VPLS instance, otherwise they will not accept or advertise routes for that VPLS.
Start a Discussions
Exhibit
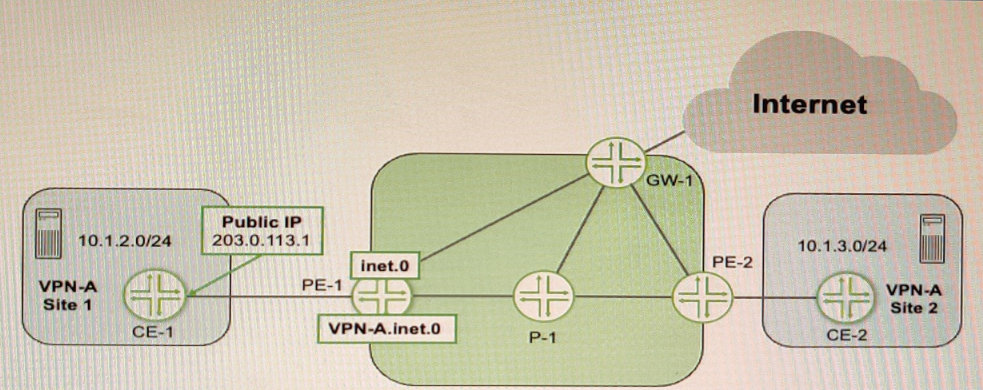
Referring to the exhibit, CE-1 is providing NAT services for the hosts at Site 1 and you must provide Internet access for those hosts
Which two statements are correct in this scenario? (Choose two.)
Correct : B, C
Start a Discussions
You are configuring a Layer 3 VPN between two sites. You are configuring the vrf-target target : 65100:100 statement in your routing instance.
In this scenario, which two statements describe the vrf-target configuration? (Choose two.)
Correct : B, D
The `vrf-target` statement in a Layer 3 VPN configuration is used to control the import and export of VPN routes by attaching a target community to the routes. This helps in defining which VPN routes should be imported into or exported from a particular VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) instance.
1. **Understanding VRF Target**:
- The `vrf-target` statement specifies the extended community attributes (route targets) that are used to control the import and export of routes in a VRF.
- These attributes help in identifying which routes should be shared between different VRFs, particularly across different PE (Provider Edge) devices.
2. **Statements Analysis**:
- **A. This value is used to identify BGP routes learned from the local CE device.**
- Incorrect. The `vrf-target` attribute is not used to identify routes learned from the local CE device. It is used to manage routes between PE devices and within the provider's MPLS network.
- **B. This value is used to identify BGP routes learned from the remote PE device.**
- Correct. The `vrf-target` value helps in identifying which routes from remote PE devices should be imported into the local VRF. It essentially acts as a filter for importing BGP routes with matching target communities.
- **C. This value is used to add a target community to BGP routes advertised to the local CE device.**
- Incorrect. Routes advertised to the local CE device do not use the `vrf-target` attribute. Instead, these routes are typically managed within the local VRF routing table.
- **D. This value is used to add a target community to BGP routes advertised to the remote PE device.**
- Correct. When advertising routes from the local PE to remote PE devices, the `vrf-target` value is added to these routes. This target community ensures that the correct routes are shared across the VPN.
**Conclusion**:
The correct statements about the `vrf-target` configuration in a Layer 3 VPN scenario are:
**B. This value is used to identify BGP routes learned from the remote PE device.**
**D. This value is used to add a target community to BGP routes advertised to the remote PE device.**
**Reference**:
- Juniper Networks Documentation on VRF Target: [VRF Target Configuration](https://www.juniper.net/documentation/en_US/junos/topics/topic-map/layer-3-vpns.html)
- MPLS and VPN Architectures by Ivan Pepelnjak and Jim Guichard
Start a Discussions
Total 96 questions